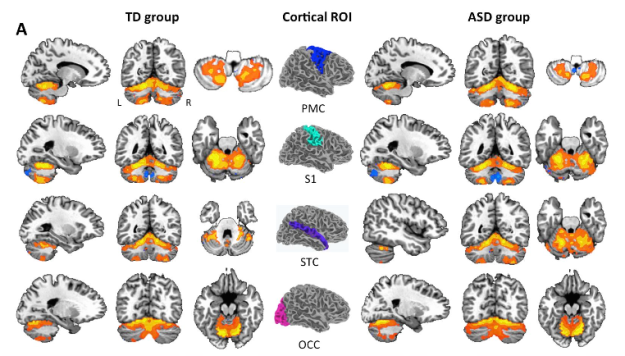
Child with autism learns new social skills via parent-mediated self-management training
A 9-year-old girl and her parents implemented self-management training so she (“Abby”) could learn to greet unfamiliar adults, not interrupt, and ask questions during conversation. One month after her parents faded out the self-management program, Abby maintained her new behaviors and generalized them to new settings. This style of intervention empowers families to improve their…