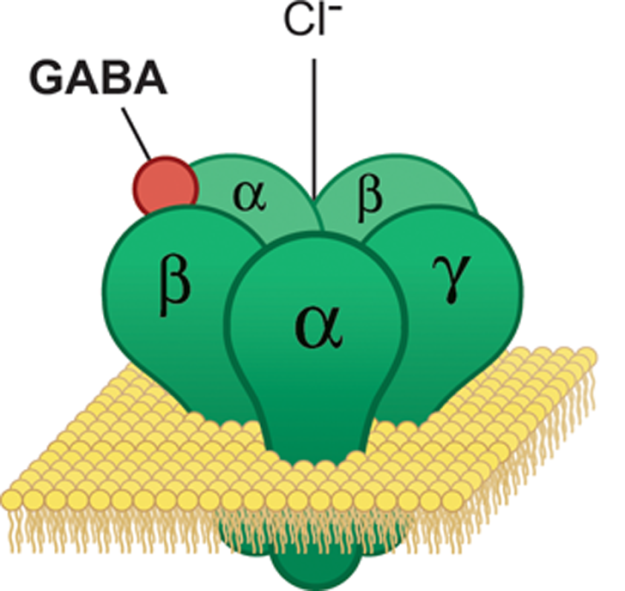
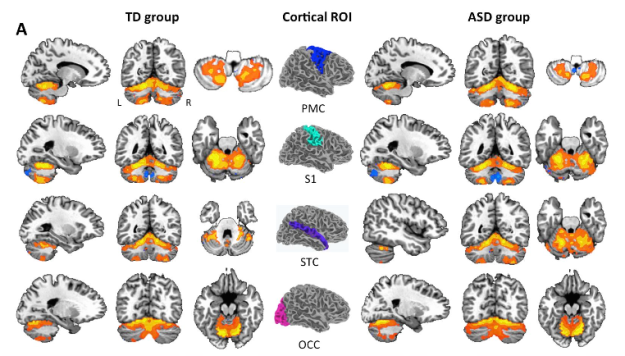
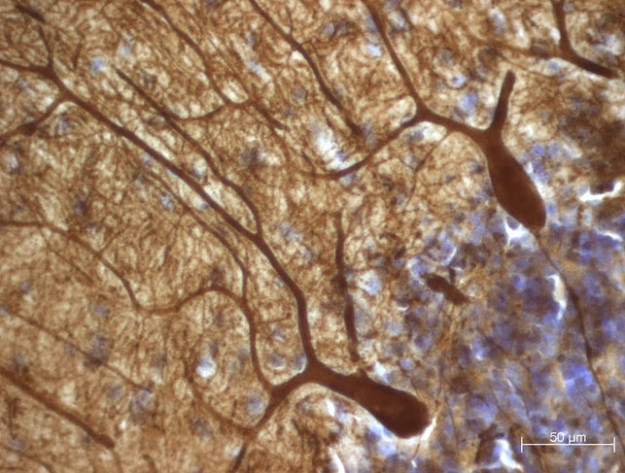
Young adults with autism increase empathic communication with training
At the Hussman Institute for Autism, we see evidence of empathy every day among people with autism. Individuals on the autism spectrum experience powerful emotions and demonstrate concern for others. Many self-advocates on the autism spectrum report being overly in-tune with the emotions of the people around them, sometimes to such a degree that it…